{{ banner_block|raw }}
What is collagen and why is it important?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in your body. It acts like scaffolding, giving structure and strength to skin, hair, nails, joints, and bones. There are several types, but Types I, II, and III are most relevant for skin elasticity, cartilage cushioning, and connective tissue strength.

It’s produced naturally by your body, using amino acids from protein-rich foods, along with nutrients like vitamin C, zinc, and copper.
Natural collagen production: How it changes with age
Unfortunately, collagen production begins to decline as early as your mid-20s. By your 40s, the process slows significantly — resulting in visible signs of aging like wrinkles, sagging skin, joint stiffness, and brittle nails.
External factors like UV exposure, smoking, and a high-sugar diet can further damage collagen and speed up this decline.
What do collagen supplements claim to do?
You’ve likely seen these promises on supplement bottles and ads:
Improved skin hydration and elasticity
Reduction in wrinkles and fine lines
Stronger hair and nails
Reduced joint pain and inflammation
Better recovery after workouts
Anti-aging support
These claims tie into major wellness trends — but do they actually hold up under scrutiny?
Do collagen supplements actually work?
Here’s the thing: when you consume collagen — whether as powder, pills, or gummies — your body breaks it down into amino acids during digestion. These amino acids are then used wherever your body needs them most.
This raises an important question: do those nutrients really get redirected to your skin, joints, or hair?
What does science say about collagen supplementation?
Studies suggest that hydrolyzed collagen (collagen peptides) can have measurable benefits — especially for skin and joint health.
A 2021 meta-analysis in International Journal of Dermatology reviewed multiple studies and found that collagen supplements improved skin hydration, elasticity, and wrinkles after 90 days of use.
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, collagen hydrolysate showed significant improvements in skin elasticity and moisture over 8 weeks.
Another study found that collagen supplements helped reduce joint pain in athletes and aging adults.
Still, results vary depending on the type of collagen, the dosage, and the individual’s lifestyle and baseline health.
Are collagen supplements safe?
Generally, yes. Collagen supplements are considered safe for most people and are well-tolerated. Reported side effects are rare and mild — usually digestive discomfort or a bad taste.
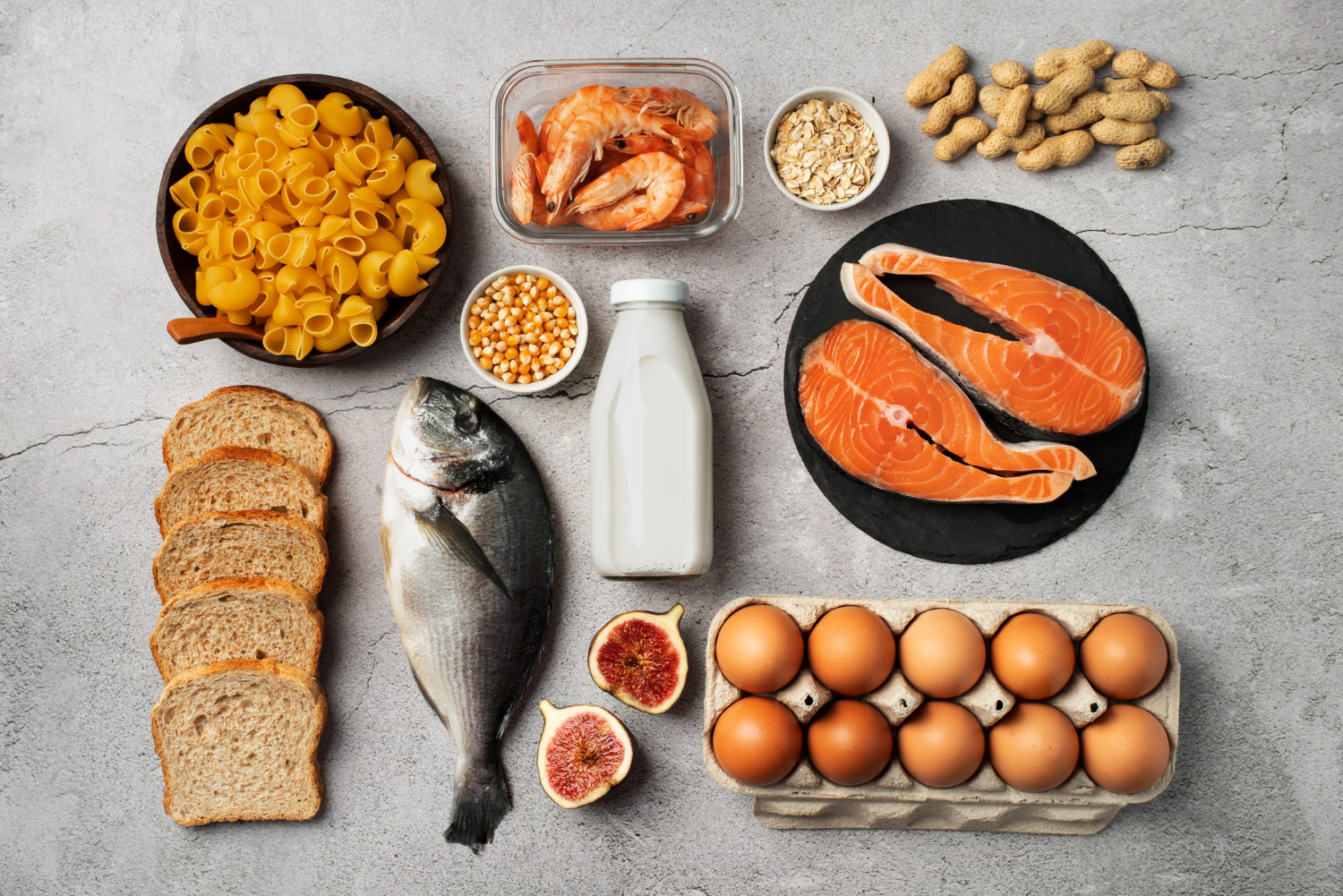
However, because they’re derived from animal sources (fish, bovine, or chicken), those with allergies or dietary restrictions should choose carefully.
Look for third-party tested brands to avoid contaminants and ensure quality.
Types of collagen and how to choose a supplement
Not all collagen is the same. Here are the key types:
Type I: Best for skin, hair, and nails
Type II: Supports cartilage and joints
Type III: Found in skin and blood vessels
Hydrolyzed collagen (collagen peptides): Easiest to absorb and most studied
Pro tip: Look for “hydrolyzed” or “collagen peptides” on the label. Pair your supplement with vitamin C to boost absorption.
Alternatives to collagen supplements
If you’d rather go the natural route, support your body’s own collagen production with:
Protein-rich foods: chicken, eggs, beans, tofu
Vitamin C sources: citrus fruits, bell peppers
Zinc and copper: nuts, seeds, shellfish
Bone broth (contains gelatin, a form of collagen)
Looking for healthy recipes? Don’t miss our helpful collection — simple, tasty, and good for you! 💚

And avoid lifestyle factors that degrade collagen — like smoking, excess sun exposure, and high-sugar diets.
Final thoughts: Are collagen supplements worth it?
So, do collagen supplements work? The short answer: yes — when taken consistently and as part of a healthy lifestyle, they can offer modest but meaningful benefits.
Scientific evidence shows improvements in skin elasticity, hydration, and joint comfort, especially with hydrolyzed collagen taken for at least 8–12 weeks. While they’re not a miracle cure, they can support aging skin and joints when combined with good nutrition and self-care.
If you’re looking to support skin health, reduce joint pain, or combat signs of aging, collagen supplements are worth trying — as long as you manage expectations and choose a high-quality product.
Sources used:
2. Effects of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation on skin aging: a systematic review and meta-analysis
















